The Agile way of working
The umbrella term that is all about making your teams great
Why Agile works in companies
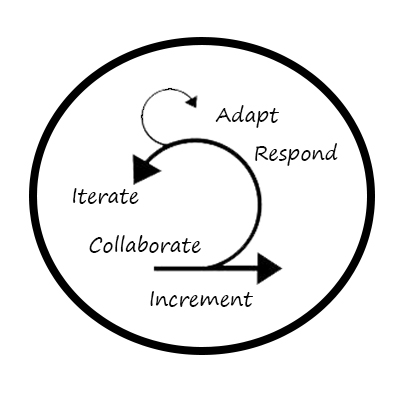
Working Agile works best in complex environments, where complex problems need to be solved. Usually this can be a simple solution, however the question is: How will you get to that simple solution? The Agile way of working has shown for many years it has great methods and frameworks to answer that question. Teams need to be able to be adaptive. Adaptive in what they do and how they deliver. They need to respond to the needs of their customer and to the changing market. To deliver their best work, they build their product in small steps, each building on the other. With an incremental flow, they will only build the things a customer wants, and the team and the customer can adapt in between. They need to collaborate, amongst themselves but also together with their stakeholders and other teams. And the work they deliver, needs to be delivered in iterations, with an inspection at the end of each iteration where delivered work can be reviewed by the customer and company standards.
The values of Agile are commitment, courage, focus, openness and respect. When teams are committed to these standards and are treated with the same, companies are transformed. Living from these values requires a change in how the whole company is looking at their people and their performance. When carried by the organization at large, barriers between people and teams will decrease and ownership will increase.
High-performing teams
Teams don't work on their own, they interact with other teams, with management, with stakeholders and other interested parties. Some teams will do great work, others are doing okay, but no more than that. Agile working is all about making your teams great, by creating the right environment for them and by enabling them to become owners of their work processes. But it's also asking for a different kind of organisation.
When you want a high-performing team, the first premisse is psychological safety. This term was first coined by Amy Edmonson, her research shows that teams can only reach their full potential if they feel free to express themselves fully. In her own words: "In a workplace, psychological safety is the belief that the environment is safe for interpersonal risk taking. People feel able to speak up when needed — with relevant ideas, questions, or concerns — without being shut down in a gratuitous way. Psychological safety is present when colleagues trust and respect each other and feel able, even obligated, to be candid." She calls for fearless organisations.
Change in the organisation
When working Agile the biggest change is that teams become self-organising and autonomous, in the newest Scrum Guide this is described as self managing teams. Getting there is asking something of the structures around the teams, management needs to accept a smaller influence in the team in exchange for a better product coming as a result. Working Agile doesn’t mean the teams can rule as they see fit, there will be guidelines from the organisation to which they need to adhere. The change in mindset that needs to take place, is that management gives a clear goal and gives the team the trust they can do it on their own. In return, the team promises to deliver that goal. They can be held accountable to that promise, they need to show happy customers, a great product made by the standards of the company. What an organisation needs to do is to create and facilitate the right circumstances for a team to deliver on that promise. Great teams don't exist alone!
Reframing to a learning mindset
Give directions to your teams to deliver their product early, also when it's still ugly and to do so often. Make the core mindset of your company learning from mistakes. If teams are unafraid of showing their unpolished diamonds, you’re on the right path. People will overcome the desire to deliver a product that has been polished to perfection and quite often turns out not to be what the customer wanted or as a product doesn’t have the impact that was foreseen. Polishing can come when you know that it’s the right product to deliver. Teams need to hear and fully understand that failing often equals to quick learning from your mistakes into a learning forward mindset. The reframing to this learning mindset needs to get done in the whole organization, everyone needs to get on board with it. It’s starts with management encouraging this failing forward, people working with the raw edits need to understand the benefit and the best leadership will show it too in their daily work.
Creating the right environment
Let your teams of experts be exactly that, experts! Encourage them to step forward and show their expertise. When you want to achieve that environment, you need to take a step back and let your team be in the lead. As their leader you don’t have to have all the knowledge, you need to know what questions to ask, to who and when. When you trust people’s decision and follow up their advice, they will take more and more ownership of what they are responsible for. In doing so, you are demonstrating situational humility, which will benefit you in this increasingly complex environment we are working in. You are paying your experts because that’s what they are. Deciding for them the finer points of how they should make something is counterproductive, you’re then taking away their feeling of confidence and responsibility. As a result they become dependent on what you decide and you cannot know it all. Trusting in their expertise is the best step you can take for increasing the value of your product.
Next thing to change is how you praise effort, regardless of the outcome. If you would apply blame to something that failed, you’re killing the learning and experimenting mindset. You can however, praise the effort to try also if the results aren’t up to standards. When clear boundaries are broken, you would act differently of course. In general though you will want to send the message that it is okay to have a different opinion and to try something new. For a fearless organization to work, the foundation is building in psychological safety. By giving people and teams their own clear responsibility and accountability, by praising the effort and celebrating the learning curve shown by mistakes, you will see your company change and have better outcomes.
The Scrum Framework
In the Agile umbrella the most used method is Scrum. It is a simple framework, with simple rules and processes in which each element is important. The Scrum Guide gives clear direction on why and by which means you can create value through adaptive solutions for complex problems.
Working Scrum means working with a steady team that has a stable budget, where it is the scope that can alter. The three roles in a team are that of Developer, Scrum Master and Product Owner, together they will have all the skills and expertise needed to do the work. The Product Owner is the linking pin in what the product should be for the end users and on what is built by the team. The Scrum Master is accountable for the Scrum Teams effectiveness and the Developers build the working product. This team learns together from experience and make their decisions on what has been observed, an empirical approach. By delivering work in an iterative and incremental way, they inspect and adapt regularly on what has been done and what still needs to be done. This requires transparency, so a team can inspect and adapt at the right moments and the important issues. This is also where the values come in again, commitment to speak the truth and deliver what you promise; focus on the agreed upon work to do; courage to speak up and do the right thing; respect for people and openness about the work and its challenges.
The cycle of inspecting, adapting and delivering increment, are done in Sprints of maximum four weeks. The events within this cycle are the Sprint Planning, where the scope for the sprint is decided on. At the Daily Stand-up that takes place every working day a renewed commitment to the goal is made, a Review of the working and usable new product is shown to the stakeholders at the end of the cycle and so is a Retrospective, a formal moment for the team to inspect the closing sprint and adapt for the new sprint. The framework of Scrum shows the best practices to build a valuable product quickly, based on more than thirty years of experience from all over the world. Paired with knowledge on transforming your organization to be fearless, by expecting high performing teams and creating the right circumstances for it, your company can be well on it’s way to achieve its best results to date.